Another thing to confirm is the state of the signals. This is shown at the bottom of the output, and on most serial interfaces can also be seen on the router's serial interface as a series of green lights. Usually when the router interface is up and normal, all of the signals will show to be up. Cisco CCNA Show IP Interfaces Brief. This tutorial explains basic show commands (such as show ip route, show ip interfaces brief, show version, show flash, show running-config, show startup-config, show controllers, etc.) in Cisco router with examples. Learn how to use show commands in Cisco router to get specific information.
Troubleshooting Using the show interfaces serial Command The output of the show interfaces serial exec command displays information specific to serial interfaces. Figure 15-1 shows the output of the show interfaces serial exec command for a High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) serial interface. Show Interface on Cisco Switches. On a Layer 2 switch we can check the status and various other counters and metrics for each physical ethernet interface or for every interface on the device. I usually start first with the following command: Switch0# show interfaces status. Physical interfaces are device ports with which the user connects devices to networks. On the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC), the user configures the phy-interface element, within the system branch, for the E-SBC to use physical interfaces. This section provides an overview of the configuration, and variations of configuration based on platform of the phy-interface element.
Cisco CCNA Configuring Router Interfaces ( Chaoter 2 Contd)
In this section you will learn how to configure interfaces on a Cisco router.
Cisco CCNA Configuring an Interface
The type of interface includes things such as serial, ethernet, fastethernet, gigabitethernet, atm, tunnel, loopback, etc.
The number, slot/number and module/slot/number are numbers used to uniquely identify an interface on different types of routers.
Cisco CCNA Configuring an Interface
Some of the configurations used to configure an interface are Network layer addresses (IP Addresses), media type, bandwidth, and other administrator commands.
Different routers use different methods to choose the interfaces used on them.
Most of today's routers are modular, the configuration would be 'interface type slot/port' or 'interface type module/slot/port'.
An example of configuring a fastethernet interface with some possible options is as follows:
interface fastethernet 0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Cisco CCNA Configuring IP Addresses
Even though you don't have to use IP on your routers, it's most often what people use. To configure IP addresses on an interface, use the ip address command from interface configuration mode.
Note: The command 'ip address
' starts the IP processing on the interface.Remember interfaces are administratively shutdown by default so you will need to perform a 'no shutdown' for the interface to come up.
Cisco CCNA Serial Interface Clocking
Cisco CCNA
Serial interfaces will usually be attached to a CSU/DSU type of device that provides clocking for the line.
But if you have a back-to-back configuration (for example, one that's used in a lab/classroom environment), on one end—the data communication equipment (DCE) end of the cable—must provide clocking.
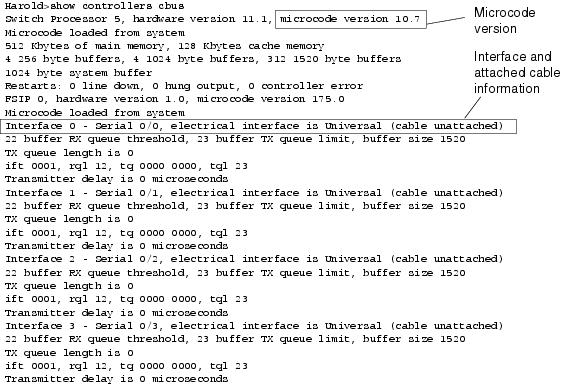
The type of cable plugged into the serial interface can be verified by performing ‘show controller' command. The clock present is representative of the cable plugged in (Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) or DCE). If it's DCE, the ‘clock rate' command will be needed in a back to back configuration.
Cisco CCNA Configuring a Serial Interface
By default, Cisco routers are all data terminal equipment (DTE) devices, so you must tell an interface to provide clocking if you need it to act like a DCE device. You configure a DCE serial interface with the clock rate command.
The 'show controllers command' displays information about the physical interface itself. It will also give you the type of serial cable plugged into a serial port. Usually, this will only be a DTE cable that plugs into a type of data service unit (DSU).
Show Interfaces Serial 020 Serial
R1# show controllers serial 0/0
Hd unit 0, idb = 0x121c04, driver structure at 0x127078
Buffer size 1524, hd unit 0, v.35 DCE cable
Fontexplorer x pro 7 0 0 9. The bandwidth and delay of an interface is used by routing protocols such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF to calculate the best cost (path) to a remote network.
So if you're using RIP routing, then the bandwidth or delay setting of an interface is irrelevant, since RIP uses only hop count to determine that.
Cisco CCNA Disabling or Enablng an Interface
You can mark an interface administratively down with the 'shutdown' command, and turn it on with the 'no shutdown' command. If an interface is shut down, it will display administratively down when using the 'show interface' command.
REMEMBER TO DO A 'NO SHUTDOWN' COMMAND WHEN YOU HAVE CONFIGURED A DEVICE….THIS TRIPS UP MANY STUDENTS ON THE SIMULATION PORTION OF THE EXAM.
Cisco CCNA Verifying Your Changes
The command 'show interface' reveals to us the hardware address (if a LAN interface), logical address, and encapsulation method, as well as statistics.
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) shows how many bytes of data can be sent in each encapsulated packet. BW is 1.544kbps by default on serial interfaces, Delay is 20,000 microseconds.
If the link is 100% reliable, the 'rely 255/255' will be shown. If the link is basically at no load , the 'load 1/255' will be displayed.
The encapsulation on a serial interface is HDLC by default. The loopback can be set to test the link and the keepalive is 10 seconds by default. This is a Data Link layer keepalive that is sent between routers. If the timers are not exactly the same, the Data Link layer will not come up.
Cisco CCNA Interpreting Interface Status
The most important statistic of the show interface command is the output of the line and>Cisco CCNA Show IP Interfaces Brief
This command is used to get a quick view of the status of all interfaces configured on the router. The status and protocol fields are quick indicators as to the state of the interface. When you are troubleshooting if you see the status as administratively down, you need to perform a 'no shutdown' on the interface to mark it administratively up. Prior to marking an interface administratively up, confirm that it should be up. Typically for security reasons unused interfaces are administratively marked down.
Cisco CCNA Which Issue on the left corresponds to the router output on the right?
Answer:
Layer 1 problem – Serial 0/1 is down, line protocol is down
Pyre 1 50427 – a party based rpg server. Layer 2 problem – Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
Layer 3 problem – no match
Port operational – Serial 0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Port disabled – Serial 0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Cisco CCNA Erasing NVRAM on a Router
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Cisco CCNA Configuring IP Addresses
Even though you don't have to use IP on your routers, it's most often what people use. To configure IP addresses on an interface, use the ip address command from interface configuration mode.
Note: The command 'ip address
' starts the IP processing on the interface.Remember interfaces are administratively shutdown by default so you will need to perform a 'no shutdown' for the interface to come up.
Cisco CCNA Serial Interface Clocking
Cisco CCNA
Serial interfaces will usually be attached to a CSU/DSU type of device that provides clocking for the line.
But if you have a back-to-back configuration (for example, one that's used in a lab/classroom environment), on one end—the data communication equipment (DCE) end of the cable—must provide clocking.
The type of cable plugged into the serial interface can be verified by performing ‘show controller' command. The clock present is representative of the cable plugged in (Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) or DCE). If it's DCE, the ‘clock rate' command will be needed in a back to back configuration.
Cisco CCNA Configuring a Serial Interface
By default, Cisco routers are all data terminal equipment (DTE) devices, so you must tell an interface to provide clocking if you need it to act like a DCE device. You configure a DCE serial interface with the clock rate command.
The 'show controllers command' displays information about the physical interface itself. It will also give you the type of serial cable plugged into a serial port. Usually, this will only be a DTE cable that plugs into a type of data service unit (DSU).
Show Interfaces Serial 020 Serial
R1# show controllers serial 0/0
Hd unit 0, idb = 0x121c04, driver structure at 0x127078
Buffer size 1524, hd unit 0, v.35 DCE cable
Fontexplorer x pro 7 0 0 9. The bandwidth and delay of an interface is used by routing protocols such as IGRP, EIGRP, and OSPF to calculate the best cost (path) to a remote network.
So if you're using RIP routing, then the bandwidth or delay setting of an interface is irrelevant, since RIP uses only hop count to determine that.
Cisco CCNA Disabling or Enablng an Interface
You can mark an interface administratively down with the 'shutdown' command, and turn it on with the 'no shutdown' command. If an interface is shut down, it will display administratively down when using the 'show interface' command.
REMEMBER TO DO A 'NO SHUTDOWN' COMMAND WHEN YOU HAVE CONFIGURED A DEVICE….THIS TRIPS UP MANY STUDENTS ON THE SIMULATION PORTION OF THE EXAM.
Cisco CCNA Verifying Your Changes
The command 'show interface' reveals to us the hardware address (if a LAN interface), logical address, and encapsulation method, as well as statistics.
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) shows how many bytes of data can be sent in each encapsulated packet. BW is 1.544kbps by default on serial interfaces, Delay is 20,000 microseconds.
If the link is 100% reliable, the 'rely 255/255' will be shown. If the link is basically at no load , the 'load 1/255' will be displayed.
The encapsulation on a serial interface is HDLC by default. The loopback can be set to test the link and the keepalive is 10 seconds by default. This is a Data Link layer keepalive that is sent between routers. If the timers are not exactly the same, the Data Link layer will not come up.
Cisco CCNA Interpreting Interface Status
The most important statistic of the show interface command is the output of the line and>Cisco CCNA Show IP Interfaces Brief
This command is used to get a quick view of the status of all interfaces configured on the router. The status and protocol fields are quick indicators as to the state of the interface. When you are troubleshooting if you see the status as administratively down, you need to perform a 'no shutdown' on the interface to mark it administratively up. Prior to marking an interface administratively up, confirm that it should be up. Typically for security reasons unused interfaces are administratively marked down.
Cisco CCNA Which Issue on the left corresponds to the router output on the right?
Answer:
Layer 1 problem – Serial 0/1 is down, line protocol is down
Pyre 1 50427 – a party based rpg server. Layer 2 problem – Serial0/1 is up, line protocol is down
Layer 3 problem – no match
Port operational – Serial 0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Port disabled – Serial 0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Cisco CCNA Erasing NVRAM on a Router
Show Interfaces Serial 020 Idm
You can delete the startup-config file by using the 'erase startup-config' command.
This command would be recommended if the router was being re-deployed or decommissioned, and you wanted to make sure none of the old configuration elements were present when it either comes back online, or is decommissioned. Once the configuration is erased, upon reboot of the router, the user will be prompted to enter setup mode as if the router had come from the factory. Setup mode can be utilized to initially configure basic things such as hostname, ip addresses on an interface, etc. If you rather entering initial configurations from regular configuration mode, you can exit out of the setup mode.
Note: The 'write erase' command is another command that performs the same function.
Cisco CCNA Draw a line From the left to the answer on the Right….
Answers:
Enter privileged EXEC mode – > enable
Enter global config mode – # configure term
Enter interface config mode – (config)# interface fa0/0
Configure the interface IP address – (config-if)# ip address 10.8.26.0 255.255.248.0
Enable the interface – (config-if)# no shutdown
Physical interfaces are device ports with which the user connects devices to networks. On the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC), the user configures the phy-interface element, within the system branch, for the E-SBC to use physical interfaces. This section provides an overview of the configuration, and variations of configuration based on platform of the phy-interface element.
Physical interface types include:
- Ethernet Management - Non-service interfaces, including:
- Primary ethernet management - IP-based access to the Command Line Interface (CLI). The interface element is often referred to as wancom0 or eth0.
- Backup ethernet management - Additional IP-based access to the CLI.
- High Availability (HA) - Connects the active E-SBC to a redundant E-SBC; the redundant E-SBC immediately resumes signaling and media service if the active fails.
- Media - Interfaces designated for signaling and media service traffic.
- Serial - Direct interface to CLI, which also displays the system's boot sequence and alarm messaging.
The user configures the primary ethernet management and the serial interfaces using boot parameters. This ensures that those interfaces are available even if there is no configuration. The user configures media and backup ethernet management interface via the primary ethernet management interface, often referred to as either eth0 or wancom0, or the serial interface after the system boots.
Interface configuration is platform dependent, with consideration of the following platform types required for successful deployment:
- Acme Packet Platforms
- Virtual Machine Platforms
- Commercial Off the Shelf (COTS) Platforms
Ethernet Management Interfaces
The primary ethernet management interface does not use the phy-interface configuration element. The E-SBC does not display the primary ethernet management interface in the configuration. Instead, the inet on ethernet boot parameter sets this interface's IP address. Backup ethernet management and HA interfaces require phy-interface configuration.
Platform considerations include:
- Acme Packet platforms:
- The system uses the slot and port configuration to identify the physical interface within the phy-interface element. Configuration recommendations include setting the phy-interface's name parameter to a value that specifies the interface, such as s0p0 (slot 0 port 0).
- The system defaults to an APIPA (RFC3927) address by default, which the user can change using the boot parameters.
- Virtual Machine platforms:
- The user must map the primary ethernet management interface and set that interfaces IP address during installation.
- The Hypervisor allows the user to map all the E-SBC management interfaces to be used during the install procedure.
- COTS platforms:
- Primary management interface is platform dependent, using the platform's integrated management application, such as ILOM, to define access to the primary management interface. Users commonly configure a static IP address on the ILOM port, which defaults to DHCP, to simplify access to the E-SBC's serial port.
- The interface-mapping tools allow the user to manage the mapping between the configured phy-interface and the platform's network interface cards on a per-MAC address basis.
Primary and backup ethernet management interfaces access the E-SBC's CLI by default. Uses can configure any or all ethernet management interfaces to carry other administrative traffic, including:
- SNMP
- SSH
- ACP/XML
- Logs sent from the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller
- Boot the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller from a remote file server
Media Interfaces
All media interfaces require a phy-interface element configuration. The phy-interface name is always required and is used in subsequent configuration, including network-interface and realm. Oracle recommends using the naming convention presented in the interface-mapping display. Further media phy-interface configuration is dependent on platform, including:
- Acme Packet platforms
- The system uses the slot and port configuration to identify the physical interface within the phy-interface element.
- Interface mapping management (MACTAB) is irrelevant.
- The phy-interface configuration for special NICs, including the Enhanced Traffic Control and Transcoding Cards, is the same as standard cards.
- Virtual Machine platforms
- The interface-mapping tools allow the user to manage the mapping between the configured phy-interface and the platform's network interface cards on a per-MAC address basis.
- Hypervisor configuration and application performance may vary based on interface architecture. Applicable architecture examples include PCI Passthrough and Paravirtualized.
- The phy-interface's name parameter only specifies the name to be used in subsequent configuration.
- The slot, port, speed, duplex and autosensephy-interface parameters are not relevant.
- The Hypervisor allows the user to map all media interfaces to be used during the install procedure.
- COTS platforms
- The interface-mapping tools allow the user to manage the mapping between the configured phy-interface and the platform's network interface cards on a per-MAC address basis.
- The phy-interface's name parameter only specifies the name to be used in subsequent configuration.
- The slot, and portphy-interface parameters are not relevant.
Serial Interface
The serial interface provides direct access to the CLI. The user can configure the E-SBC's serial interface using boot parameters, which configure port output and speed. Platform-dependent detail includes:
Show Interfaces Serial 020 Sezon
- Acme Packet platforms - Serial access is available via one of two physical ports, depending on platform.
- Virtual Machine platforms - Virtual serial interface access is typically provided directly by the hypervisor. Boot parameters are irrelevant.
- COTS platforms - Virtual serial access is available from the integrated management application.
Refer to the High Availability chapter in this document for configuration description and procedures of HA interfaces. Refer to your release-specific Installation and Platform Preparation Guide for description and procedures on configuring boot parameters and using the interface-mapping tools. Monit 1 2 1.

